大家好,我是指北君。
前几天我的朋友小 B 给他女神在面试的时候支招,问到 ArrayList 就说是用数组实现的。最后女神被面试官要求手写 ArrayList。小 B 惨遭被分手。小 B 感到非常委屈,ArrayList 不就是数组么。 ArrayList 其实可以对面试官说他的扩容,默认容量,各个方法的时间复杂度等等,这样面试成功的机率比只是数组的竞争对手大了 50%。
构造函数
ArrayList 有三个构造函数,默认不带参数的构造函数就是初始化一个空数组。
1 | |
带一个 int 类型的容量参数的构造函数,可以指定 ArrayList 的容量大小。
1 | |
带一个集合的构造函数, 将集合转换成 Object[] 类型后拷贝到 elementData 中。
1 | |
常用函数
add()
先从 ArrayList 最常用的方法 add() 开始讲起,add() 方法就是将元素添加到 elementData 的末尾。平均时间复杂度为 O(1)。
1 | |
- 扩容的大小为原长度+1/2的原长度
- 如果扩容长度比传入的最小容量小,则使用最小容量,如果扩容长度超过设定的最大容量,则实际用最大容量
- 初始化默认长度为10,当添加到11个长度时,容量为15
add(int index, E element)
将元素插入到指定的位置,主要的操作是将指定位置之后的元素往后移动一个位置,空出 index 位置。平均时间复杂度为 O(n)。
1 | |
get()
get() 应该是第二个常用的函数,可以返回随机位置的元素。需要注意的是越界时,超过容量返回的是 IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常,index 太小返回的是 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 异常。平均时间复杂度为 O(1)。
1 | |
remove()
删除指定位置的元素,并返回删除的元素。平均时间复杂度为 O(n)。
1 | |
remove(Object o)
删除指定的元素,需要循环数组删除第一个指定的元素。平均时间复杂度为 O(n)。
1 | |
总结
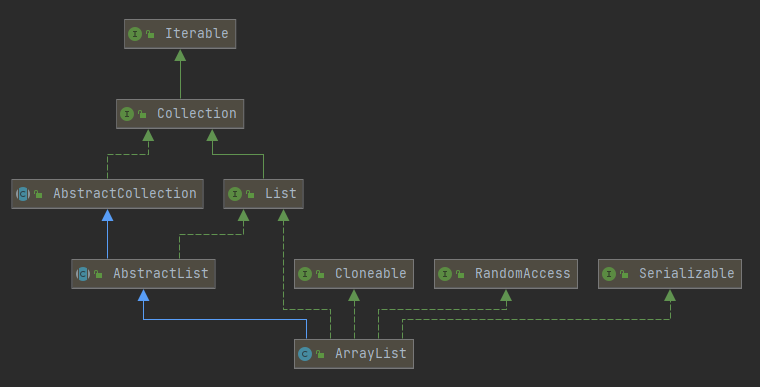
- ArrayList 内部用一个数组存储元素,容量不够时会扩容原来的一半。
- ArrayList 实现了 RandomAccess,支持随机访问。
- ArrayList 实现了 Cloneable,支持被拷贝克隆。
- ArrayList 删除指定元素和指定位置上的元素的效率不高,需要遍历数组。
我是指北君,操千曲而后晓声,观千剑而后识器。感谢各位人才的:点赞、收藏和评论,我们下期更精彩!
