哈喽,大家好,我是指北君。
本篇文章给大家介绍基于树实现的数据结构——TreeMap
1、TreeMap 定义
听名字就知道,TreeMap 是由Tree 和 Map 集合有关的,没错,TreeMap 是由红黑树实现的有序的 key-value 集合。
PS:想要学懂TreeMap的实现原理,红黑树的了解是必不可少的!!!
1 | |
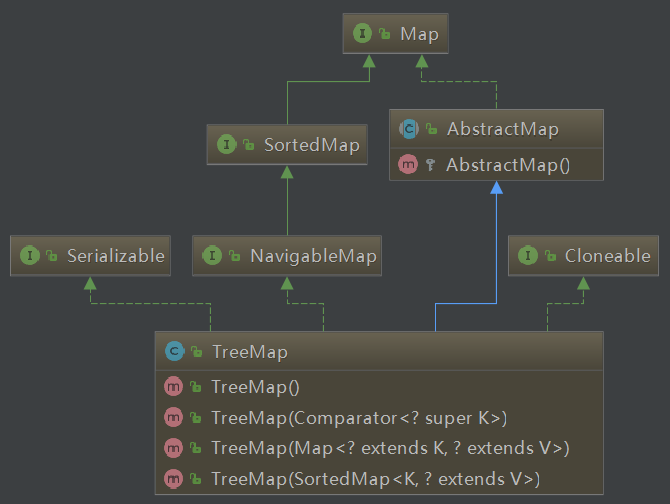
TreeMap 首先继承了 AbstractMap 抽象类,表示它具有散列表的性质,也就是由 key-value 组成。
其次 TreeMap 实现了 NavigableMap 接口,该接口支持一系列获取指定集合的导航方法,比如获取小于指定key的集合。
最后分别实现 Serializable 接口以及 Cloneable 接口,分别表示支持对象序列化以及对象克隆。
2、字段定义
①、Comparator
1 | |
可以看上面的英文注释,Comparator 是用来维护treemap集合中的顺序,如果为null,则按照key的自然顺序。
Comparator 是一个接口,排序时需要实现其 compare 方法,该方法返回正数,零,负数分别代表大于,等于,小于。那么怎么使用呢?这里举个例子:
这里有一个Person类,里面有两个属性pname,page,我们将该person对象放入ArrayList集合时,需要对其按照年龄进行排序。
1 | |
打印结果为:

②、Entry
1 | |
对于Entry详细源码这里不列举了,主要看几个字段:
1 | |
相信对红黑树这种数据结构了解的人,一看这几个字段就明白了,这也印证了前面所说的TreeMap底层有红黑树这种数据结构。
③、size
1 | |
用来表示entry的个数,也就是key-value的个数。
④、modCount
1 | |
基本上前面讲的在ArrayList,LinkedList,HashMap等线程不安全的集合都有此字段,用来实现Fail-Fast 机制,如果在迭代这些集合的过程中,有其他线程修改了这些集合,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
⑤、红黑树常量
1 | |
3、构造函数
①、无参构造函数
1 | |
将比较器 comparator 置为 null,表示按照key的自然顺序进行排序。
②、带比较器的构造函数
1 | |
需要自己实现Comparator。
③、构造包含指定map集合的元素
1 | |
使用该构造器创建的TreeMap,会默认插入m表示的集合元素,并且comparator表示按照自然顺序进行插入。
④、带 SortedMap的构造函数
1 | |
和上面带Map的构造函数不一样,map是无序的,而SortedMap 是有序的,使用 buildFromSorted() 方法将SortedMap集合中的元素插入到TreeMap 中。
4、添加元素
1 | |
添加元素,如果初始化TreeMap构造函数时,没有传递comparator类,是不允许插入key==null的键值对的,相反,如果实现了Comparator,则可以传递key=null的键值对。
另外,当插入一个新的元素后(除了根节点),会对TreeMap数据结构进行修正,也就是对红黑树进行修正,使其满足红黑树的几个特点,具体修正方法包括改变节点颜色,左旋,右旋等操作,这里我不做详细介绍了.
5、删除元素
①、根据key删除
1 | |
删除节点分为四种情况:
1、根据key没有找到该节点:也就是集合中不存在这一个节点,直接返回null即可。
2、根据key找到节点,又分为三种情况:
①、待删除节点没有子节点,即为叶子节点:直接删除该节点即可。
②、待删除节点只有一个子节点:那么首先找到待删除节点的子节点,然后删除该节点,用其唯一子节点顶替该节点。
③、待删除节点有两个子节点:首先找到该节点的中序后继节点,然后把这个后继节点的内容复制给待删除节点,然后删除该中序后继节点,删除过程又转换成前面①、②两种情况了,这里主要是找到中序后继节点,相当于待删除节点的一个替身。
6、查找元素
①、根据key查找
1 | |
7、遍历元素
通常有下面两种方法,第二种方法效率要快很多。
1 | |
8、小结
好了,这就是JDK中java.util.TreeMap 类的介绍。
我是指北君,操千曲而后晓声,观千剑而后识器。感谢各位人才的:点赞、收藏和评论,我们下期更精彩!
